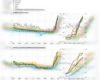Sunday, July 7, 2024 11:26 AM
Japanese Companies Lead Wage Increases Amid Economic Recovery
- Japanese companies raise wages in response to labor shortages and inflation
- Discrepancy in wage hikes between major corporations and smaller firms
- Efforts to bridge wage gap and stabilize prices for economic growth
 Image Credits: thefrontierpost
Image Credits: thefrontierpostJapanese companies are increasing wages to combat labor shortages and inflation, aiming for economic recovery and income equality through bridging the wage gap.
Japanese companies have recently made the most substantial wage increases in over three decades, according to the country's largest union. This surge in wages is a response to labor shortages and rising inflation, which are impacting household finances. On average, workers can anticipate a 5.10% increase in their monthly pay this fiscal year, as per a survey by the union group Rengo.
The outcome of the spring labor negotiations, known as 'shunto,' is crucial for Japan's economic recovery efforts. Policymakers are striving for a strong and sustainable economic rebound, aiming to counter the effects of increasing living costs with higher household income and spending. However, there exists a gap between large corporations and smaller firms regarding wage hikes. While major companies with over 300 union-supported employees raised wages by 5.19%, smaller enterprises experienced a more modest increase of 4.45%.
A more robust growth path in Japan's fragile economy could lead to a definitive end to deflation and potentially prompt the Bank of Japan (BOJ) to consider further interest rate hikes as part of its monetary policy normalization strategy. Recent surveys indicate an overall rise in wages, with expectations for real wages to turn positive by the middle of the year as inflation stabilizes.
In mid-March, prominent firms announced a substantial pay raise of 5.28%, marking the most significant increase since Japan's economic bubble burst in the 1990s. This development coincided with the BOJ's decision to discontinue its negative interest rates and yield curve control policy. With major corporations finalizing their wage adjustments for the year, attention is now shifting towards the possibility of wage hikes extending to smaller businesses, which are struggling to pass on increased costs to customers.
Approximately 70% of Japan's workforce is employed by small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Efforts are underway to bridge the wage gap, focusing on enhancing pricing competitiveness for small firms to facilitate a 5% wage increase next year. The government is also urged to intensify measures to stabilize prices and the currency, especially given the yen's depreciation, which has raised import costs and strained households.
As part of initiatives to address income inequality, Prime Minister Fumio Kishida's administration has committed to raising the minimum hourly wage to 1,500 yen ($9.27) by the mid-2030s, up from the current average of around 1,000 yen.
The significant wage increases by Japanese companies reflect a response to labor shortages and inflation, aiming to bolster household finances. As the economy strives for recovery, the focus is on bridging the wage gap between large corporations and smaller businesses. With efforts to stabilize prices and enhance competitiveness, the future holds prospects for improved economic conditions and income equality in Japan.