Tuesday, July 2, 2024 03:20 PM
Pakistan's Current Account Deficit Shrinks Significantly in FY2024
- Current account deficit in Pakistan drops to US $0.5 billion in FY2024.
- Financial account sees net inflows of US $4.2 billion in FY2024.
- Remittances grow by 3.5% in July-April FY2024, reaching US $23.8 billion.
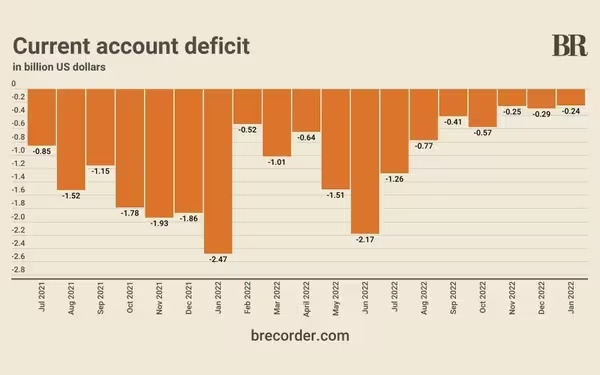 Image Credits: Business Recorder
Image Credits: Business RecorderThe current account deficit in Pakistan has significantly decreased in FY2024, leading to improved financial stability and trade dynamics. Remittances have also shown growth, reflecting positive economic trends.
The current account deficit in Pakistan has witnessed a remarkable decline, dropping to US $0.5 billion from July to March in the fiscal year 2024, compared to US $4.1 billion in the same period the previous year. This positive development is credited to the effective measures implemented by the government despite facing challenges in the global economic landscape. The reduction in the current account deficit has played a crucial role in stabilizing external pressures and mitigating risks associated with external financing challenges.
During the July-March period of fiscal year 2024, Pakistan's external account has made significant progress, with the current account deficit shrinking by 87.5 percent to US $0.5 billion from US $4.1 billion in the previous year. The financial account also experienced net inflows of US $4.2 billion, primarily driven by inflows from friendly nations and official sources, marking a substantial shift from the net outflows of US $1.1 billion in the same period of FY2023.
The reduction in the current account deficit, coupled with financial assistance from bilateral and multilateral partners, has resulted in the accumulation of foreign reserves, which surged to US $8.0 billion by the end of March 2024 from US $4.4 billion at the end of FY2023. This enhanced performance of the external sector, along with the bolstering of foreign reserves, has instilled confidence in the Pakistani currency.
Global merchandise trade experienced a 5 percent decline in 2023, totaling US $24.01 trillion, attributed to a global economic slowdown, trade fragmentation, and geopolitical tensions. Despite challenges, the World Trade Organization (WTO) projects a growth of 2.6 percent in global merchandise trade for 2024 and 3.3 percent for 2025, highlighting potential risks such as geopolitical tensions, protectionism, policy uncertainties, and supply disruptions.
As Pakistan's external account continued to improve significantly in July-April FY2024, the current account deficit narrowed by 94.8 percent to US $0.2 billion compared to US $3.9 billion in the same period the previous year. The trade deficit for goods decreased by 21.6 percent to US $17.7 billion in July-April FY2024 due to a substantial decline in imports. However, the services account deficit rose to US $1.9 billion in the same period, primarily due to a sharp increase in services imports.
The primary income account deficit also increased by 34.8 percent to US $6.1 billion in July-April FY2024, driven by higher dividend repatriation and interest payments. Remittances grew by 3.5 percent during this period, reaching US $23.8 billion, compared to US $23.0 billion in the previous year, attributed to structural reforms in trade and payments.
The positive trends in Pakistan's external account reflect the country's efforts to strengthen its economic position and enhance financial stability. The significant reduction in the current account deficit, coupled with increased foreign reserves and improved trade dynamics, bode well for Pakistan's economic outlook. As global trade faces challenges and opportunities, Pakistan's proactive measures and strategic partnerships position it favorably in the evolving international economic landscape.













